Impact of HIV and AIDS
The CDC estimates the total number of Americans living with HIV as of 2016, the last year with good public health statistics, at 1,008,929 (CDC, 2019a). Of those, 156,300 (12.8%) are unaware of their infection (CDC, 2019a).
Latest Statistics (CDC, 2019a) United States 2016 Worldwide 2018
HIV annual new cases 38,700 1,800,000
Total estimated living with HIV/AIDS 1,008,929 37,900,000
Annual AIDS deaths 15,807 770,000
CDC reports indicate that the estimated incidence of new HIV infections has stabilized at about 39,000 per year (CDC, 2019a). The number of new cases discovered annually has achieved relative stability still results in a progressive annual increase in the total number of HIV infections. Theories behind this center around HIV sufferers living longer due to the advent of new treatments, resulting in an ever-expanding number of active HIV cases both in the United States and worldwide (Bennett, 2019).
Gay, bisexual and other men who have sex with men (MSM)* of all races and ethnicities, particularly young to middle-aged Black/African American MSM, remain the population most profoundly affected by HIV (CDC, 2019a). In 2017, the estimated number of new HIV infections among MSM was 25,748, a number identified as relatively stable from 2012 through 2017 (CDC, 2019a).
Other behaviors warrant following by public health include (CDC, 2019a):
Injection drug use in all sex and age groups shows around 2,389 known new HIV diagnoses in 2017.
MSM sexual activities simultaneous with injection drug use show a large enough presentation of new HIV diagnoses to be categorized by the CDC separately, at 1,252 cases in 2017.
Heterosexual contact of all ages in 2017 revealed a 9,170 new HIV diagnosis rate.
Black/African Americans continue to experience the most severe burden of HIV compared with other races and ethnicities. Black/African Americans represent approximately 13% of the United States population but accounted for an estimated 43% of new HIV infections in 2017. They also accounted for 42% of individuals living with HIV infection (CDC, 2019c).
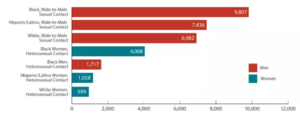
New HIV Diagnoses in the US and Dependent Areas for the Most-Affected Subpopulations, 2017 (CDC, 2019a).
Hispanics/Latinos represented approximately 18% of the United States population and accounted for 26% of new HIV infections in 2016. New infections rose by around 30% among Latino and Hispanic MSM, from 6,400 to 8,300 in 2016. The greatest rise was among 25 to 34-year-olds, where new infections increased by 68% (Avert, 2019).
White men having sex with men runs in third place of new HIV diagnosis, with around 6,982 reported new cases in 2017 (CDC, 2019a).
Heterosexual African American/black women, young people, and transgender women of all ethnicities are also disproportionately affected (Avert, 2019).